SEPTOPLASTY
Unveiling the Mystery: A Deep Dive into Septoplasty
Septoplasty, a surgical procedure correcting a deviated septum, offers relief from various breathing difficulties. This detailed summary delves into its purpose, preparation, steps, benefits, risks, and recovery to equip you with comprehensive knowledge.
The Crooked Culprit:
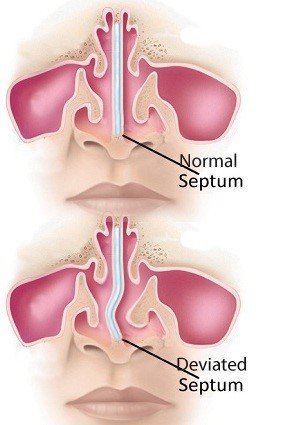
The septum, a thin wall, divides your nose into two nostrils. A deviated septum is one that’s bent or off-center, causing various airflow disruptions.
Why Fix It?
A deviated septum can lead to:
- Difficulty breathing: Blocked nostrils impede proper air intake and worsen with activities like sleeping.
- Facial pressure and pain: Pressure buildup can cause discomfort and headaches.
- Snoring and sleep apnea: Reduced airflow disrupts sleep patterns, potentially leading to sleep apnea.
- Postnasal drip and congestion: Blocked sinuses due to poor drainage cause recurring irritation and discharge.
- Frequent sinus infections: Stagnant air can make you more susceptible to infections.
Preparing for the Journey:
- Pre-operative assessment: Your doctor will discuss your concerns, medical history, and perform a physical examination to assess the septum deviation and suitability for surgery.
- Imaging tests: X-rays or CT scans may be used to visualize the septum’s structure.
- Blood tests: Routine blood tests may be required to assess your overall health.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about any medications you take, especially blood thinners.
- Fasting: You may be required to fast for several hours before the surgery.
The Surgical Steps:
- Anaesthesia: General anaesthesia is typically used to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Incision: An incision is made inside the nose to access the septum.
- Cartilage and bone reshaping: Excess cartilage or bone is carefully removed or repositioned to straighten the septum.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or dissolvable stitches.
- Packing: Nasal packs may be inserted temporarily to support the septum as it heals.
The Road to Recovery:
- Hospital stays: Depending on the complexity, you may stay overnight or be discharged on the same day.
- Pain management: Medications will be provided to manage any discomfort.
- Nasal packing removal: The packs are typically removed within a few days after surgery.
- Swelling and bruising: Expect some swelling and bruising around the nose, subsiding within 1-2 weeks.
- Nasal discharge and crusting: This is normal and usually clears up within a few weeks.
- Activity restrictions: Avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks to promote healing.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns.
The Upsides of Fixing the Crooked:
- Improved breathing: The main benefit, often leading to significant relief from nasal congestion and difficulty breathing.
- Reduced facial pressure and pain: Eliminates pressure build-up and associated discomfort.
- Reduced snoring and sleep apnoea: Improved airflow can significantly reduce snoring and potentially resolve sleep apnoea.
- Decreased sinus issues: Better drainage reduces the risk of postnasal drip and recurrent infections.
- Overall improved quality of life: Breathing easier and sleeping better often leads to a significant improvement in well-being.
Potential Bumps on the Road:
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding after surgery is common but usually self-resolves.
- Infection: Though rare, proper hygiene and follow-up care minimize the risk.
- Numbness or loss of smell: Temporary or permanent changes in smell or taste are rare but possible.
- Septal perforation: A hole in the septum is rare but may require further treatment.
Remember:
- Septoplasty is a safe and effective procedure with high success rates.
- The decision to undergo surgery depends on the severity of your symptoms and potential benefits outweighing the risks.
- Open communication with your doctor is crucial to discuss your concerns and expectations.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with your healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment planning based on your specific situation.
FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)
Unveiling the Mystery: A Deep Dive into Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at improving drainage and ventilation of the sinuses, offering relief from chronic sinusitis and its associated symptoms. This detailed summary delves into its purpose, preparation, steps, benefits, risks, and recovery to equip you with comprehensive knowledge.
Understanding the Blockade:
The sinuses are air-filled cavities surrounding the nose and eyes. Chronic sinusitis occurs when these cavities become inflamed and filled with mucus, leading to various unpleasant symptoms. Blockages may be caused by:
- Swollen nasal tissues: Allergies, infections, or structural abnormalities can contribute to tissue swelling.
- Nasal polyps: Soft, painless growths that can obstruct sinus drainage.
- Deviated septum: A crooked septum can hinder proper airflow and drainage.
Why Go Under the Scope?
FESS offers several advantages over traditional sinus surgery:
- Minimally invasive: Uses thin, lighted instruments inserted through the nostrils, minimizing incisions and tissue disruption.
- Precise targeting: Allows visualization and removal of specific blockages while preserving healthy tissue.
- Faster recovery: Shorter hospital stay and quicker return to normal activities.
- Reduced risk of complications: Less bleeding and potential for injury compared to traditional surgery.
Preparing for the Journey:
- Pre-operative assessment: Your doctor will discuss your symptoms, medical history, and perform a physical examination to determine the extent of your sinusitis and suitability for FESS.
- Imaging tests: CT scans or X-rays provide detailed images of your sinuses and surrounding structures.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking, especially blood thinners.
- Fasting: You may be required to fast for several hours before the surgery.
The Surgical Steps:
- Anaesthesia: General anaesthesia is typically used to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Microscope positioning: A high-resolution binocular microscope provides magnified visualization of the nasal cavity and sinuses.
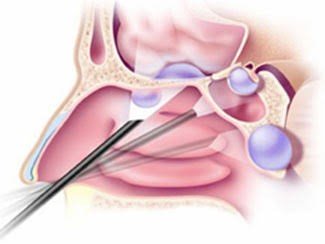
- Endoscope insertion: Thin, flexible instruments equipped with cameras and lights are inserted through the nostrils.
- Blockage removal: Using specialized tools, the surgeon carefully removes polyps, inflamed tissues, or other obstructions.
- Sinus drainage openings: Drainage pathways within the sinuses may be widened or enlarged to improve airflow and mucus clearance.
- Closure: No external incisions are needed, and the nasal passages may be packed temporarily to support healing.
The Road to Recovery:
- Hospital stays: Depending on the complexity, you may stay overnight or be discharged on the same day.
- Pain management: Medications will be provided to manage any discomfort.
- Nasal packing removal: The packs are typically removed within a few days after surgery.
- Swelling and bruising: Expect some swelling and bruising around the nose and eyes, subsiding within 1-2 weeks.
- Nasal discharge and crusting: This is normal and usually clears up within a few weeks.
- Nasal saline irrigation: Regular saline rinses help clear mucus and promote healing.
- Activity restrictions: Avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks to promote healing.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns.
The Rewards of Opening the Gates:
- Reduced sinus symptoms: Relief from congestion, facial pressure, pain, headaches, and postnasal drip.
- Improved breathing: Enhanced airflow for easier and more comfortable breathing.
- Reduced risk of future infections: Better drainage minimizes the risk of recurring sinusitis.
- Improved sleep quality: Reduced congestion can significantly improve sleep quality.
- Overall improved quality of life: Relief from persistent symptoms can significantly enhance well-being.
Potential Bumps on the Road:
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding after surgery is common but usually self-resolves.
- Infection: Though rare, proper hygiene and follow-up care minimize the risk.
- Numbness or loss of smell: Temporary or permanent changes in smell or taste are rare but possible.
- Eye injuries: Very rare, but potential complications during surgery can affect the eyes.
Remember:
- FESS is a safe and effective procedure with high success rates.
- The decision to undergo surgery depends on the severity and duration of your symptoms, and whether other treatments haven’t provided sufficient relief.
- Open communication with your doctor is crucial to discuss your concerns and expectations.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with your healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment planning based on your specific situation.
SEPTORHINOPLASTY
Delving Deep: A High-Detail Summary of Septorhinoplasty
Septorhinoplasty is a combined surgical procedure addressing both functional and aesthetic concerns of the nose. This detailed summary explores its purpose, preparation, steps, benefits, risks, and recovery to empower you with comprehensive knowledge.
Understanding the Needs:
- Septoplasty: Corrects a deviated septum, the cartilage and bone dividing the nostrils, improving breathing difficulties like congestion, sleep apnea, and facial pressure.
- Rhinoplasty: Reshapes the external nose to address aesthetic concerns like bumps, asymmetry, or size discrepancies, aiming for facial harmony and improved self-confidence.
Planning for the Transformation:
- Pre-operative consultation: Discuss your goals, medical history, and expectations with your surgeon. They’ll perform a physical examination and may recommend imaging tests.
- Discuss anaesthetic options: General anaesthesia is typically used for comfort and safety.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about any medications you take, particularly blood thinners.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking well before surgery promotes healing and reduces risks.
The Surgical Journey:
- Anaesthesia: You’ll be comfortably asleep during the procedure.
- Incisions: Depending on the approach, incisions may be made inside the nose (closed rhinoplasty) or on the columella (skin between the nostrils) and along the base of the nose (open rhinoplasty).
- Septoplasty: The surgeon addresses the deviated septum, straightening it using cartilage or bone modifications.
- Rhinoplasty: Reshaping involves trimming, repositioning, or adding cartilage and bone to achieve the desired nose structure.
- Closure: Incisions are meticulously closed with sutures or dissolvable stitches.
- Splints or packing: Nasal splints or packing may be used temporarily to support the septum and new shape.
Road to Recovery:
- Hospital stays: Depending on the complexity, you might stay overnight or be discharged on the same day.
- Pain management: Medications will be provided to manage discomfort.
- Swelling and bruising: Expect swelling and bruising around the nose and eyes, peaking within 2-3 days and subsiding gradually.
- Nasal discharge and crusting: This is normal and usually clears up within a few weeks.
- Nasal saline irrigation: Regular saline rinses help clear mucus and promote healing.
- Activity restrictions: Avoid strenuous activities for several weeks to promote healing.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular checkups are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Blossoming Benefits:
- Improved breathing: Septoplasty relieves nasal congestion, sleep apnea, and facial pressure.
- Enhanced aesthetics: Rhinoplasty improves facial harmony, boosts self-confidence, and potentially alleviates concerns about the nose’s appearance.
- Combined benefits: Addressing both functional and aesthetic concerns in one surgery can be more efficient and cost-effective.
Potential Challenges:
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding after surgery is common but usually self-resolves.
- Infection: Though rare, proper hygiene and follow-up care minimize the risk.
- Numbness or loss of smell: Temporary or permanent changes are rare but possible.
- Unsatisfactory results: Revision surgery may be needed if results don’t meet expectations.
Remember:
- Septorhinoplasty is a complex procedure with high success rates when performed by a qualified surgeon.
- The decision to undergo surgery depends on individual factors, severity of concerns, and potential risks vs. benefits.
- Open communication with your surgeon is crucial throughout the process.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with your healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment planning based on your specific situation.
BALLOON SINUPLASTY
Balloon Sinuplasty: A Minimally Invasive Approach to Clear Blocked Sinuses
Balloon sinuplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), a condition characterized by inflammation and blockage of the sinuses. It offers an alternative to traditional sinus surgery for suitable patients.
Who Can Benefit from Balloon Sinuplasty?
Balloon sinuplasty is an option for individuals experiencing:
- Chronic Sinusitis Symptoms: These include facial pain or pressure, congestion, runny nose, postnasal drip, and difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Inadequate Response to Medication: If medical treatments like antibiotics and nasal corticosteroids haven’t provided sufficient relief for chronic sinusitis symptoms.
- Limited Sinus Blockage: Balloon sinuplasty is most effective for blockages in the maxillary, frontal, and sphenoid sinuses (not the ethmoid sinuses).
How Balloon Sinuplasty Works:
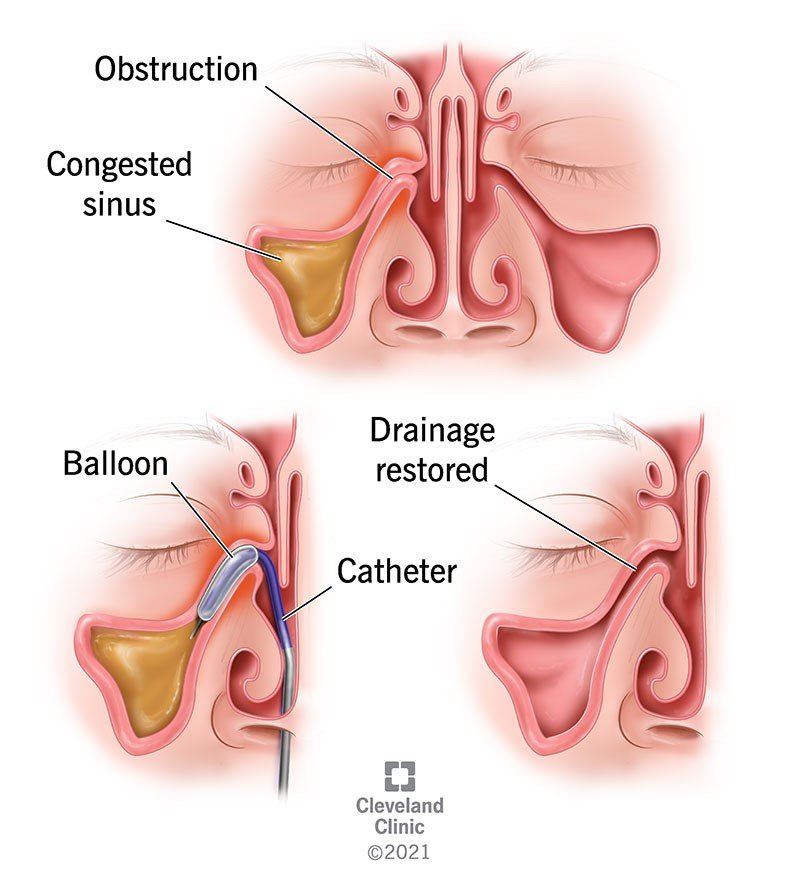
- Catheter Insertion: The doctor inserts a thin, flexible catheter with a balloon tip into the nostril and guides it to the blocked sinus opening (ostia).
- Balloon Inflation: The balloon is inflated with a precise amount of pressure to gently widen the ostia, improving drainage and airflow within the sinus cavity.
- Micro-fractures: The inflation process may create tiny micro-fractures in the surrounding bone, further facilitating drainage.
- Balloon Deflation and Removal: Once adequate dilation is achieved, the balloon is deflated and removed from the sinus cavity.
Advantages of Balloon Sinuplasty:
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to traditional sinus surgery, balloon sinuplasty is less invasive, requiring no cutting or removal of bone or tissue.
- Outpatient Procedure: Balloon sinuplasty can often be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
- Faster Recovery: The recovery time for balloon sinuplasty is typically shorter than traditional sinus surgery, with less discomfort and pain.
- Preserved Mucosal Lining: Unlike traditional surgery, balloon sinuplasty preserves the sinus’ natural mucosal lining, which plays a role in preventing infection.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: The minimally invasive nature of the procedure reduces the risk of complications associated with traditional surgery.
Things to Consider:
- Not for All Cases: Balloon sinuplasty is not suitable for all cases of chronic sinusitis, particularly those with severe blockage or involvement of the ethmoid sinuses.
- Success Rates: While generally successful, balloon sinuplasty may not provide long-term relief for everyone. Some individuals may require repeat procedures or additional treatments.
- Consultation with an Otolaryngologist: Consulting with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist, also known as an otolaryngologist, is crucial to determine if balloon sinuplasty is the right option for your specific situation.
Overall, balloon sinuplasty offers a promising minimally invasive approach for treating chronic sinusitis. If you’re experiencing persistent sinus problems and haven’t found relief with medication, discuss this option with your doctor to see if it’s a suitable solution for you.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult with your healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment planning based on your specific situation.